- 03 Oct 2021
- Dan
- Reviews
- Comments: 0
Recent advances in medical technology have enabled medical professionals to improve the safety and efficacy of wound closure procedures and nerve reconstruction surgeries. Innovations such as tissue engineering techniques, improved suture materials and techniques, and robotic-assisted procedures allow medical professionals to minimize complications associated with these surgeries. This article will provide an overview of recent innovations in wound closure and nerve reconstruction and discuss the potential implications for patients.

One of the most exciting developments in wound closure is tissue engineering. This technique involves using biodegradable scaffolds that can be seeded with cells to repair or replace damaged tissues. These scaffolds have been used to close large wounds and repair nerves and other tissues in the body. Additionally, tissue engineers are now developing ways to produce skin grafts by 3D bioprinting. This technology has the potential to revolutionize wound closure and nerve reconstruction, as it could provide more precise control of grafts to reduce healing time and improve outcomes.
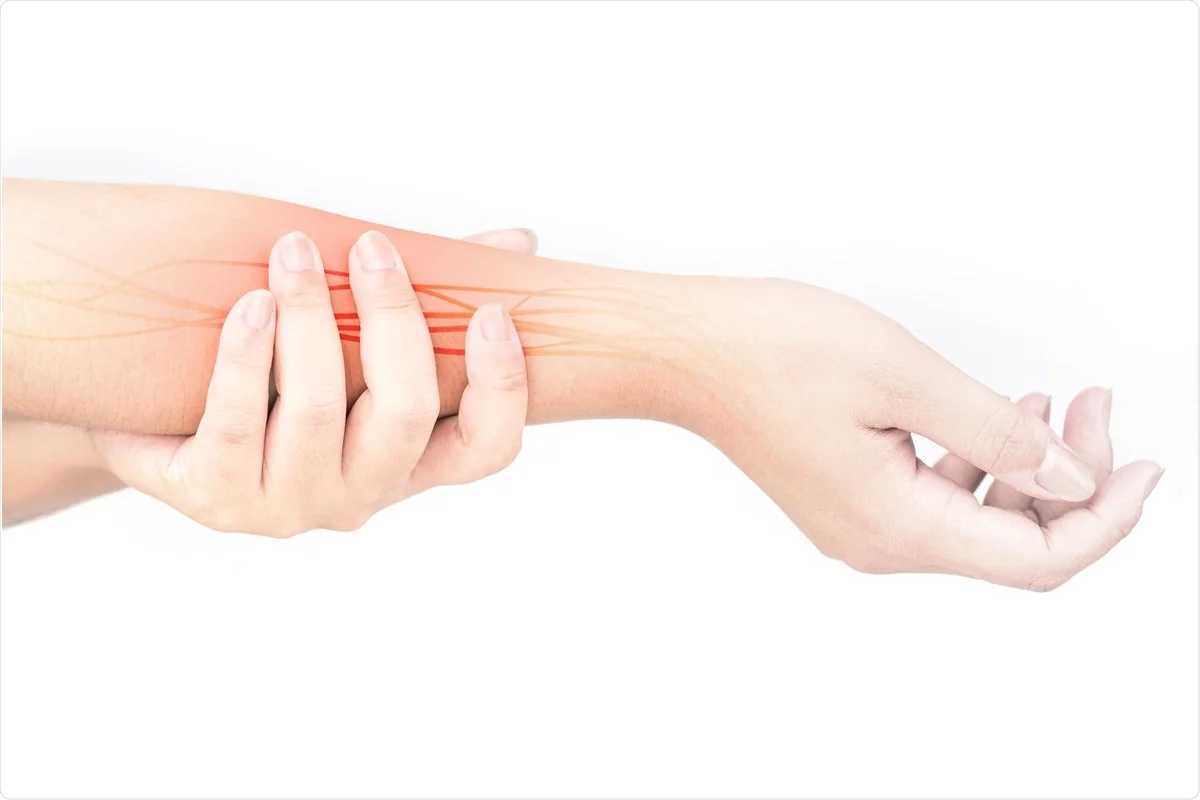
Nerve repair devices are also a promising development in nerve reconstruction. These devices bridge gaps between damaged nerves, allowing them to heal faster and more completely. They also reduce the risk of scar tissue formation, which can decrease nerve sensitivity and other long-term complications.
Improved suturing materials and techniques also play a key role in minimizing complications during wound closure. For example, synthetic absorbable sutures can reduce the risk of infection and provide better tissue healing. Additionally, new suturing techniques, such as laparoscopic suturing, allow for less scarring and a shorter recovery time.
Robotic-assisted procedures are increasingly being used in wound closure and nerve reconstruction surgeries. Robotic systems can provide more precise needle placement and suturing control, resulting in better outcomes. Additionally, they can reduce the time needed for a procedure and minimize complications.

Hi, I’m Dan and I write blogs for businesses. I’ve been doing this since 1994 and have written over 10,000 blog posts (and counting). I love writing about what you’re passionate about and how to make your business successful. So if you want to know more about blogging or social media marketing, just let me know!